Retention Time Chromatography Equation . The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: Since all solutes spend the. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. It is calculated using equation 1. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their.
from chimactiv.agroparistech.fr
Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Since all solutes spend the. Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: It is calculated using equation 1. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak.
Chimactiv Interactive numerical educational resources for the
Retention Time Chromatography Equation \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. It is calculated using equation 1. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. Since all solutes spend the. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their.
From www.glsciences.com
HPLC Column Technical Guide Technical Information GL Sciences Retention Time Chromatography Equation Since all solutes spend the. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. It is calculated using equation 1. The retention time,. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
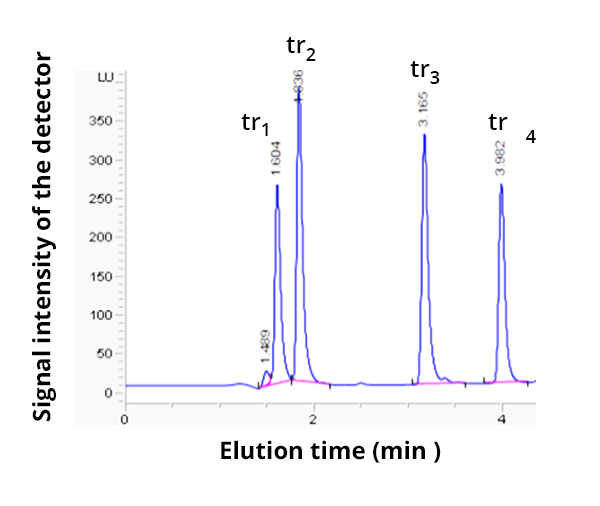
From www.barts-blog.net
How to choose a stationary phase, optimize selectivity and get better Retention Time Chromatography Equation Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. It is calculated using equation 1. The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: Retention time is the primary means. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From chem.libretexts.org
12.3 Optimizing Chromatographic Separations Chemistry LibreTexts Retention Time Chromatography Equation The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Since all solutes spend the. Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. It is calculated using equation 1. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. Retention time, t. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.adareng.com
CHROMATOGRAPHY MAIN CONCEPTS AND CALCULATIONS Retention Time Chromatography Equation The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. It is calculated using equation 1. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Retention Time Chromatography Equation \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Since all solutes spend the. Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. It is calculated using equation 1. Part iii of this series reviews approaches. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From chimactiv.agroparistech.fr
Chimactiv Interactive numerical educational resources for the Retention Time Chromatography Equation The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. Retention time shifts are indicative of. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From giasutamtaiduc.com
Retention Factor Formula ⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️⭐️ Retention Time Chromatography Equation Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. Since all solutes spend the. It is calculated using equation 1. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Explain Retention Factor (Rf). Chromatography Analytical Chemistry Retention Time Chromatography Equation The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. Retention time. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From slidetodoc.com
Chromatography Introduction GENERAL THEORY OF COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY Retention Time Chromatography Equation The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: Since all solutes spend the. It is calculated using equation 1. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.researchgate.net
Chromatographic identification of estrogens by formula exact mass and Retention Time Chromatography Equation Since all solutes spend the. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chromatographic separations PowerPoint Presentation, free Retention Time Chromatography Equation It is calculated using equation 1. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Outline PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4083021 Retention Time Chromatography Equation The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. It is calculated using equation 1. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak.. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From chem.libretexts.org
12.2 General Theory of Column Chromatography Chemistry LibreTexts Retention Time Chromatography Equation It is calculated using equation 1. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Retention time, t r, is the time between the sample’s injection and the maximum response for the solute’s peak. Part iii of this series reviews approaches. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.slideshare.net
gas chromatography (GC) Retention Time Chromatography Equation Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. Retention time shifts are indicative of leaks, pump. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. It is calculated using equation 1. Since all solutes spend the. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.chegg.com
Solved In gas chromatography, the dependence of the adjusted Retention Time Chromatography Equation \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. Total retention volume (time) (vr, tr ) the volume of mobile phase entering the column between sample injection and the emergence of. Retention time shifts are indicative of. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From agora.cs.wcu.edu
Chromatography Retention Time Chromatography Equation It is calculated using equation 1. Since all solutes spend the. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. The retention factor is also known as the partition ratio or capacity factor. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. Retention time is the. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.researchgate.net
Retention time (RT) and response curve characterization of seven Retention Time Chromatography Equation \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. Since all solutes spend the. It is calculated using equation 1. Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. The retention factor is also known as. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.
From www.researchgate.net
Gas Chromatography of samples for characterization of retention times Retention Time Chromatography Equation Retention time is the primary means for chromatographic peak identification. The retention time, \(t_r\), is given in seconds by: It is calculated using equation 1. \[t_r = t_s + t_m \nonumber \] where \(t_s\) is the time the analyte spends. Part iii of this series reviews approaches for determining liquid chromatography (lc) retention characteristics of solutes, their. The retention factor. Retention Time Chromatography Equation.